本文
Overview of the Economy of Ehime Prefecture
Economic Overview
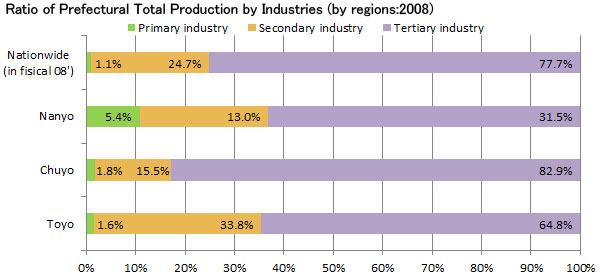
As a result of its geography and history, Ehime Prefecture is traditionally divided into three regions: Toyo (Eastern area), Chuyo (Central area), and Nanyo (Southern area). Each region has developed distinct industrial clusters.
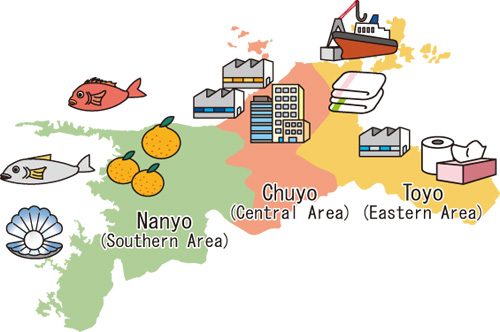
Toyo (Eastern Area)

With a variety of factories, Toyo has played a leading part in the manufacturing industry in Ehime Prefecture. Shikokuchuo City, for instance, is one of the foremost paper related manufacturing areas. One factory of a comprehensive paper manufacturing company in this area has the highest output of paper and paperboard in all of Japan. There are also a number of small to medium paper and paper processing manufacturers in the area.
In Niihama and Saijo cities, there are a number of large corporations involved in the production of basic materials for manufacturing, as well as companies involved in the manufacturing or assembling of chemicals, metals, machinery and electronics. Also emerging in recent years are high-tech industries related to electronics, fine chemicals and biotechnology. The more established steel and beer manufacturing industries are also building new facilities.
In Imabari City, a local company boasts the highest ship-building production in Japan. Another company produces more than 50% of the towels manufactured nationwide. As well, a company that manufactures cold cathode discharge lamps used for LCD back lights has the highest production in the world. There is also a major petroleum refinery and a food manufacturer that produces the highest volume in Japan of seasoning sauces used for such things as grilled meat.
Chuyo (Central Area)

Chuyo is the center of politics and economy. The prefectural capital, Matsuyama City, is in the Chuyo area.
Also in Chuyo are major manufacturers such as a company that produces world class carbon and aramid fiber, a major boiler and farming machine, an electronics maker that boasts the highest production volume of blood sugar sensors in Japan, and the number 1 producer of dried bonito flakes and seasoning sauces.
Also thriving in the Chuyo area is the marine product processing industry that produces such things as a delicacy made using small fish. Other industries include tourism which take advantage of such well known attractions as Dogo hot springs and Matsuyama Castle, and a traditional pottery industry producing items such as Tobe-yaki.
Nanyo (Southern Area)

Agriculture, forestry and fisheries are flourishing in Nanyo taking advantage of the mild climate and the bountiful blessings of nature.
The area is famous as a top class producer of mandarin oranges and a variety of other citrus fruit as well as aquaculture (e.g., yellow tail, sea bream, etc.), and the cultivation of pearls. Other related industries are fish processing, such as minced and steamed fish called ‘kamaboko’ and fried fish paste called ‘jakoten’. In recent years, fish processing companies are thriving with the increased demand for fish fillets from cultured fish - some of which are exported.
There are also a variety of unique companies such as a company that was the first to produce fish meat sausage, a confectionery manufacturer that makes traditional and western style sweets, a company that makes fancy wooden boxes, and the number 1 producer of party crackers.
|
Items |
Amount (million yen) |
|---|---|
|
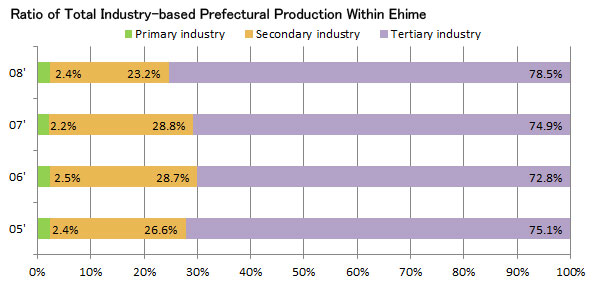
Prefectural gross product (nominal) |
4,631,968 |
|
Primary industry |
102,816 |
|
Secondary industry |
1,067,859 |
|
Tertiary industry |
3,642,328 |
|
Prefectural income |
3,336,066 |
|
Per capita prefectural income |
232,300yen (2008) |
|
Items |
Number of people |
Ration |
|---|---|---|
|
Ehime Prefecture |
760,000 |
- |
|
Primary industry |
60,000 |
80% |
|
Secondary industry |
220,000 |
290% |
|
Tertiary industry |
480,000 |
637% |
|
Number of agriculture management |
33,177 (2010) |
|---|---|
|
Number of forestry management |
3,875 (2010) |
|
Number of fishery management |
5,009 (2008) |
|
Number of industrial management |
2,550 (2009) |
|
Number of commercial management |
19,600 (2007) |
Economy of Ehime

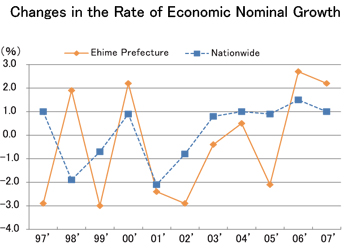
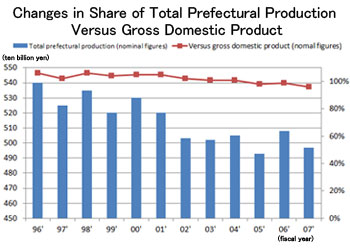
The prefectural income of Ehime is approximaTely 1% of Japan's national income. Thus, it is called the "1% economy".
Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration in Progress

In Ehime Prefecture, academic, business and governmental groups collaborate to form a network whose purpose is creating new business and industry.
One example is the regional regeneration consortium R&D project which is underway at Ehime Industrial Promotion Foundation in Matsuyama City, where the seeds of new technology developed at Ehime University are used by companies and the prefectural industrial technology center working together as the basis for new businesses.
Another collaboration example is in Niihama City, where companies in the eastern region are joining hands around Toyo Industrial Creation Center to do research and development for the urban area industry-university-government cooperation projects.
As well, a number of collaboration projects are taking place with small to medium sized companies cooperating with large business entities, university and public research institutes to develop new products, technology or construction methods. As part of a strategic approach, companies based in the prefecture are also being encouraged to create new businesses or open up new markets with the help of trading companies and financial institutions.
Leading-Edge Advanced Research and Development

For the first time in the world, Professor Yaeta Endo of Ehime University has succeeded in developing a practical application of cell-free protein synthesis that can synthesize protein in test tubes.
This technology can be applied from microorganisms to higher animals maintaining high quality and high efficiency.
It is expected that this technology will be used in a variety of fields such as the medical, environmental and energy sectors.
*At the Cell-free Science and Technology Research Center at Ehime University, research is being conducted that studies methods of cell-free protein synthesis. This research has been part of a number of entrepreneurial ventures outside of the university.